Addressing the challenge of patient outmigration and sustainable growth
Patient outmigration presents a significant challenge for rural and critical access hospitals, leading to financial strain, decreased community trust, and difficulties in maintaining essential services. Factors such as limited provider availability, poor perception of quality of care, and referral patterns contribute to patients traveling out of market for care.
The impact of patient outmigration on rural health care
- Financial loss: Rural hospitals lose revenue when patients seek care elsewhere, making it harder to sustain and expand services.
- Service reductions: As fewer patients utilize local services, hospitals may struggle to justify maintaining access to certain specialties, services, or facilities.
- Community health risks: Increased travel times for health care can delay treatment, reduce preventive care, and impact overall population health.
 |
Leveraging data to combat outmigration
The key to reversing outmigration is understanding why and where it happens. By utilizing market data and analytics tools, rural hospitals can identify patient migration trends, pinpoint service gaps, and make strategic decisions to improve retention.
1. Identifying outmigration patterns
Using market data and patient journey analytics, rural hospitals can determine:
- The most common types of patients that are seeking care outside their health system
- Which service lines are most affected by outmigration
- Referral patterns that influence patient movement
- The financial impact of outmigration, including lost revenue
2. Strengthening high -demand service lines
With data-driven insights, rural hospitals can:
- Increase patient access, promotions, and outreach strategies to better inform the community about the services that are offered locally
- Build partnerships with larger health systems for collaborative care models
- Enhance telehealth offerings to retain patients who might otherwise leave for specialty care and/or coordinate with larger health systems for post-operative care management (e.g., physical therapy, follow-up visits). This approach brings care closer to home, reducing patient travel times and expenses related to gas, hotel stays, and parking.
3. Data-driven patient retention strategies
Rural hospitals that proactively analyze and act on patient outmigration data can:
- Develop targeted marketing campaigns to educate the community about available services, especially those that have been prone to higher rates of outmigration
- Improve physician communication to ensure they as well as their patients are aware of care options within their community
- Optimize patient experience to build trust and encourage local care utilization
Data in action: Market outmigration analysis
Rural hospitals that have implemented data-driven strategies have successfully reduced outmigration by aligning their strategic development initiatives and resources with community needs.
Looking at the market outside of Madison, Wis., an analysis of patient outmigration trends shows that approximately 6,000 patients leave the Sauk County, Wis., market each year to receive care elsewhere. Notably, more than 50 percent of these cases are being captured by two Madison-based hospitals, with orthopedic services seeing the highest percentage of outmigration.
For hospitals in this market, strategic outreach and marketing initiatives could be deployed to retain more orthopedic patients locally. Highlighting competitive advantages over larger city hospitals — such as reduced travel time, easier parking, quicker appointment access, and improved patient care coordination — can help rural hospitals attract and retain more patients within their own communities.
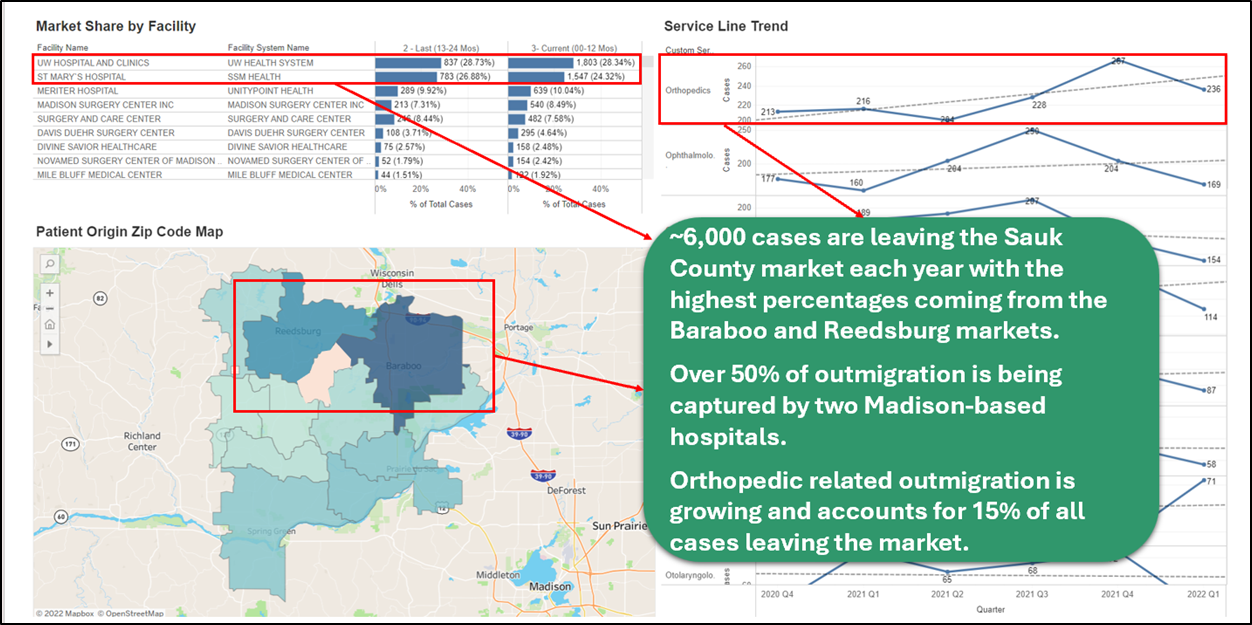 |
Drilling down further into service line trends, orthopedic-related outmigration is the most significant, accounting for 15 percent of all cases leaving the market. This highlights a key service gap that rural hospitals in the region may need to address to retain more patients.
By leveraging this type of data, hospitals can pinpoint opportunities to enhance service offerings, strengthen referral networks, and implement targeted patient retention strategies.
Looking ahead: The role of data in rural health care sustainability
The future of rural health care depends on proactive strategies that keep care local. Actionable data empowers hospital leaders to make informed decisions, optimize resources, and ensure long-term viability. By understanding and addressing patient outmigration trends, rural hospitals can strengthen their role as primary health care providers within their communities.
Learn more about how Intellimed’s data solutions help rural hospitals analyze patient outmigration and drive strategic growth.
NRHA adapted the above piece from Intellimed, a trusted NRHA partner, for publication within the Association’s Rural Health Voices blog.
 | About the author: Adam Tiedt, regional vice president at Intellimed, is an award-winning health care strategy leader with over 12 years of experience in the industry. Adam excels at partnering with rural hospital executive leaders to support data-driven strategic development initiatives. |
